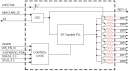
Features
- PCIe Gen1–4 compliant
- Integrated terminations provide 100Ω differential Zo: reduced component count and board space
- 1.8V operation: reduced power consumption
- Outputs can optionally be supplied from any voltage between 1.05V and 1.8V: maximum power savings
- OE# pins: support DIF power management
- LP-HCSL differential clock outputs: reduced power and board space
- Programmable slew rate for each output: allows tuning for various line lengths
- Programmable output amplitude: allows tuning for various application environments
- DIF outputs blocked until PLL is locked: clean system start-up
- Selectable 0%, -0.25% or -0.5% spread on DIF outputs: reduces EMI
- External 25MHz crystal; supports tight ppm with 0ppm synthesis error
- Configuration can be accomplished with strapping pins: SMBus interface not required for device control
- 3.3V tolerant SMBus interface works with legacy controllers
- Space-saving 6 × 6 mm 48-VFQFPN; minimal board space
- Selectable SMBus addresses: multiple devices can easily share an SMBus segment
- Available in AEC-Q100 qualified, Grade 2 (-40°C to +105°C) version (wettable flank package)
Description
The 9FGV0841 is an 8-output very low power clock generator for PCIe Gen1–4 applications with integrated output terminations providing Zo=100 Ω. The device has 8 output enables for clock management and supports 2 different spread spectrum levels in addition to spread off.
For information regarding evaluation boards and material, please contact your local IDT sales representative.
Parameters
| Attributes | Value |
|---|---|
| Diff. Outputs | 8 |
| Diff. Output Signaling | LP-HCSL |
| Output Freq Range (MHz) | 25 - 25, 100 - 100 |
| Power Consumption Typ (mW) | 62 |
| Supply Voltage (V) | 1.8 - 1.8 |
| Output Type | LP-HCSL, LVCMOS |
| Xtal Freq (MHz) | 25 - 25 |
| Diff. Termination Resistors | 0 |
| Package Area (mm²) | 36 |
| Battery Backup | No |
| Battery Seal | No |
| CPU Supervisory Function POR | No |
| Crystal Frequency Trimming | No |
| Frequency Out Pin | No |
| Inputs (#) | 1 |
| Input Freq (MHz) | 25 - 25 |
| Function | Generator |
| Input Type | Crystal, LVCMOS |
| Core Voltage (V) | 1.8 |
| Output Voltage (V) | 0.8V, 1.8V |
| Product Category | Automotive Timing, PCI Express Clocks |
Package Options
| Pkg. Type | Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | Lead Count (#) | Pitch (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VFQFPN | 6.0 x 6.0 x 0.9 | 48 | 0.4 |
Application Block Diagrams
 | Connected Android-Based Vehicle Instrument Cluster Android-based automotive cockpit with wireless connectivity and real-time displays. |
 | Communication Gateway & Integrated DVR/DMS System Integrated automotive gateway merging CoGW with DVR/DMS video processing. |
 | Automotive Cockpit System with Haptics Advanced cockpit system with next-generation haptics, BroadLED driver, and PMIC. |
 | Tire Pressure Monitoring System Low-power Bluetooth LE TPMS design with integrated PMIC for cost, size, and development time reduction. |
 | Full Graphics Cluster & Cockpit System High-efficiency display system to support a full graphics cluster in automotive cockpits. |
 | High-End Cockpit & Infotainment Solution |
 | Full-Function HMI with 4K Video Support High-performance HMI design delivers seamless 4K video, advanced graphics, and reliable connectivity. |
 | Full-function HMI with FHD Video Support Full-function HMI platform features a high-performance MPU and offers built-in USB 3.0, PCI Express, and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces. |
Applied Filters: