The year 2015 introduced a new era of power management as high-profile devices began to adopt USB-C ports. A true all-in-one port, it can deliver bidirectional data and power at the same time. With the popularity of the USB-C universal power adaptor standard, it allows buyers to use a common adaptor for various applications and go green, saving money and space.
USB-C charging requires a fundamental change to the existing power delivery architecture and presents a new challenge to system designers. With a default 5V voltage, the USB-C port can negotiate with the plugged-in device to raise the port voltage to 12V, 20V, or another mutually agreed-on voltage, at a mutually agreed current level. The maximum power a USB-C port can deliver is 20V at 5A current, which is 100W of power. There are many emerging applications where the voltage level is required to operate beyond the 20V standard USB-C maximum voltage. One such example is a printer motor using 24V and 32V, that requires a boost conversion technology to implement and enable the turbo boost USB Power Delivery (PD) voltage to get the desired higher voltage. Renesas provides a Winning Combination reference design (see Figure 1) to give engineers a design that will help them achieve all these requirements.
Let’s explore the concept of the design. The R9A02G011 USB Power Delivery controller is based on the Universal Serial Bus (USB) Power Delivery Specification Revision 3.0 and USB Type-CTM Cable and Connector Specification Revision 1.3. The PD controller performs negotiations for more current and/or higher voltages over the USB cable (VBUS) than what is defined in the USB 2.0, USB 3.0 or BC 1.2 specifications, and controls circuitry to select a local power source or power sink. The R9A02G011 uses a 300kbps BMC modulated signal through the CC wire in the USB Type-CTM.
The ISL81401A is a unidirectional 4-switch synchronous buck-boost controller with peak and average current sensing and monitoring at both ends to provide the turbo boost function and boost the USB PD voltage to a higher voltage. The USB PD with turbo boost reference design can achieve as high as 32V which can deliver up to 45W maximum output power.
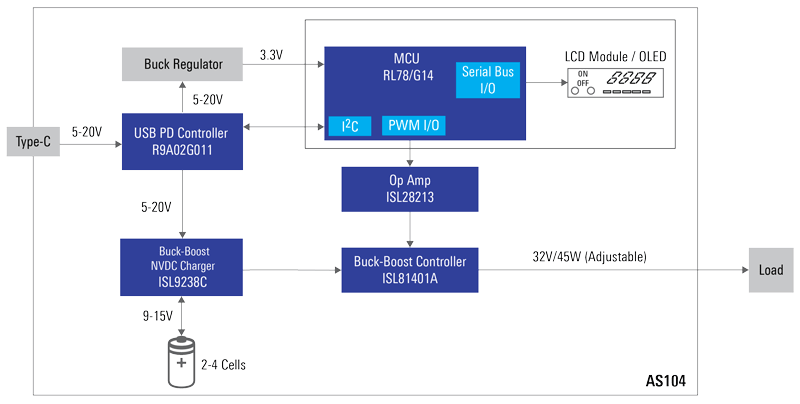
Figure 1. USB PD with Turbo Boost Reference Design
The ISL9238C is a buck-boost Narrow Output Voltage DC (NVDC) charger. It provides NVDC charging for 2-, 3- or 4-cell Li-ion batteries and supports kick-start applications where inrush current becomes critical during power-up. It also protects against system collapse, due to inadequate power from the USB PD, by utilizing the supplemental charge from the battery on start-up. The ISL28213 is a dual channel general-purpose micropower, rail-to-rail input and output operational amplifier, which works with the external LCD module, based on an RL78/G14 MCU, to output PWM channels and control the output voltage setting.
With this reference design, Renesas provides an option for a compact, robust and cost-effective solution that is suitable for numerous industrial and consumer applications.
Visit the winning combinations page to see more solutions that help our customers accelerate their designs to get to market faster.

