特長
- PCIe Gen1-4準拠
- 終端の内蔵により100Ωの差動Zoを実現:部品点数と基板面積を削減
- 1.8V動作:消費電力の低減
- OE#端子:DIFパワーマネージメント対応
- LP-HCSL差動クロック出力:消費電力と基板面積の削減
- 各出力のプログラマブルスルーレート:様々な線長に対応したチューニングが可能
- プログラマブル出力振幅:様々なアプリケーション環境に対応したチューニングが可能
- PLLがロックされるまでのDIF出力ブロック:クリーンシステムスタートアップ
- 0%、-0.25%、-0.5%から選択可能なDIF出力スプレッド:EMIの低減
- 外付け25MHz水晶振動子、0ppmの合成エラーでタイトなppmをサポート
- ストラップピンによるコンフィギュレーションが可能:デバイス制御のためのSMBusインターフェースは不要
- レガシーコントローラ対応3.3V SMBusインタフェース
- 省スペース4x4mm 24ピンVFQFPN、最小限の基板スペースを実現
説明
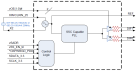
9FGV0241は、PCIe Gen1-4 アプリケーション向けの2出力超低電力周波数ジェネレータで、Zo=100 Ωの出力終端を内蔵しています。 クロック管理用に2つの出力イネーブルを備え、スペクトラム拡散オフに加えて、2種類のスペクトラム拡散レベルをサポートします。
パラメータ
| 属性 | 値 |
|---|---|
| Diff. Outputs | 2 |
| Diff. Output Signaling | LP-HCSL |
| Output Freq Range (MHz) | 25 - 25, 100 - 100 |
| Power Consumption Typ (mW) | 45 |
| Supply Voltage (V) | 1.8 - 1.8 |
| Output Type | LP-HCSL, LVCMOS |
| Xtal Freq (MHz) | 25 - 25 |
| Diff. Termination Resistors | 0 |
| Package Area (mm²) | 16 |
| Battery Backup | No |
| Battery Seal | No |
| CPU Supervisory Function POR | No |
| Crystal Frequency Trimming | No |
| Frequency Out Pin | No |
| Inputs (#) | 1 |
| Input Freq (MHz) | 25 - 25 |
| Function | Generator |
| Input Type | Crystal, LVCMOS |
| Core Voltage (V) | 1.8 |
| Output Voltage (V) | 0.8V, 1.8V |
| Product Category | PCI Express Clocks |
パッケージオプション
| Pkg. Type | Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | Lead Count (#) | Pitch (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VFQFPN | 4.0 x 4.0 x 0.9 | 24 | 0.5 |
アプリケーション・ブロック図
 | 自動光学検査(AOI) DRP-AIおよびWi-Fi 6をサポートする強力なMPUにより、高速で低遅延のAOIシステムを実現します。 |
 | 複数のPHYを搭載したスマートホームコントローラ マルチスタンダードPHY、直感的なコントロール、将来を見据えた設計を備えたオールインワンスマートホームゲートウェイ。 |
 | Arm Cortex-A53搭載の産業用オートメーションプラットフォーム この産業用オートメーションプラットフォームは、iMX8シリーズのアプリケーションプロセッサを含むArm Cortex-A53 MPU向けに設計されています。 |
 | 高性能ヒューマンマシンインタフェース(HMI)システム 幅広いヒューマンマシンインタフェース機能を駆動するための汎用性の高いシステムオンモジュール(SoM)。 |
適用されたフィルター