特長
- PCIe Gen1-4準拠
- 終端内蔵LP-HCSL出力;標準的なPCIeデバイスと比較して24個の抵抗を節約可能
- 標準消費電力54mW;熱に関する懸念を低減
- 出力はオプションで1.05〜1.8Vの任意の電圧から出力可能;最大限の省電力を実現
- OE#ピン;DIFパワーマネージメント対応
- 各出力のプログラマブルスルー・レート;様々な線長に合わせたチューニングが可能
- プログラマブル出力振幅;様々な使用環境に合わせたチューニングが可能
- PLLがロックされるまでのDIF出力;クリーンなシステムスタートアップ
- 0%、-0.25%、-0.5%から選択可能なDIF出力スプレッド;EMIの低減
- 外付け25MHz水晶振動子、0ppmの合成エラーでタイトなppmをサポート
- ストラップピンによるコンフィギュレーションが可能;デバイス制御にSMBusインタフェースは不要
- 3.3 VトレラントSMBusインタフェースは、レガシーコントローラに対応
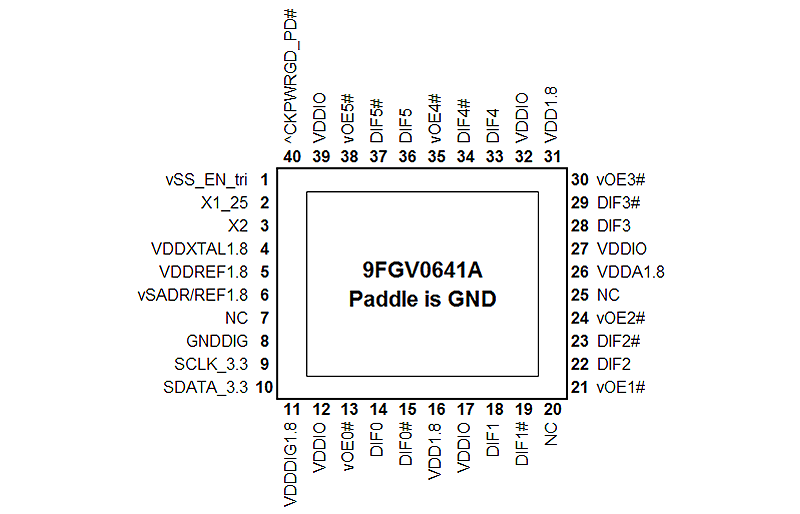
- 省スペースな5×5mm 40ピンVFQFPN;最小限の基板スペースを実現
- 選択可能なSMBusアドレス;複数のデバイスでSMBusセグメントを簡単に共有可能
説明
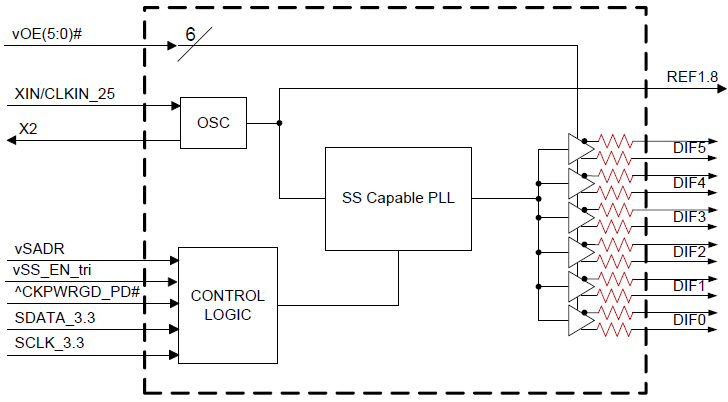
9FGV0641は、ルネサスのSOC対応 1.8V超低消費電PCIeクロックファミリーのひとつです。 このデバイスは100Ωの出力終端を内蔵しており、100Ωの伝送ラインに方向性を持たせて接続することができます。 また、クロック管理用に6つの出力イネーブルを備え、スペクトラム拡散オフに加えて2種類のスペクトラム拡散レベルにも対応しています。
評価ボードや材料に関する情報は、お近くの販売代理店にお問い合わせください。
パラメータ
| 属性 | 値 |
|---|---|
| Temp. Range (°C) | -40 to 85°C, 0 to 70°C |
パッケージオプション
| Pkg. Type | Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | Lead Count (#) | Pitch (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| VFQFPN | 5.0 x 5.0 x 0.9 | 40 | 0.4 |
アプリケーション・ブロック図

|
AI 搭載のスケーラブルな HMI SMARC SoM
マルチコア処理、高度なグラフィックス、スマートHMIのための安定な接続性を備えたスケーラブルなSoM。
|

|
高性能ヒューマンマシンインタフェース(HMI)システム
幅広いヒューマンマシンインタフェース機能を駆動するための汎用性の高いシステムオンモジュール(SoM)。
|

|
マルチディスプレイHMI SoM
消費電力とタイミングを最適化したSOMは、マルチディスプレイの組み込みアプリケーションをサポートします。
|
適用されたフィルター
フィルター
ソフトウェア/ツール
サンプルコード
シミュレーションモデル
Ron Wade, chief PCIe system architect explains the fundamental difference in reference clock jitter budgets between the first three generations of the specification and those of Gen4 and Gen5 which raise new challenges for designers.
Related Resources
This whiteboard video presents a brief overview comparing the evolution of PCI Express data rates through five generations versus that of the common clock jitter specifications.
Renesas's chief PCIe system architect explains how to derive separate reference clock jitter limits from the PCI Express Gen4 and Gen5 specifications.
A detailed overview of IDT's full-featured PCI Express (PCIe) clock and timing solutions. The presentation addresses PCIe Gen 1, Gen 2, Gen 3, and Gen 4 architectures and how IDT's industry-leading solutions provide all the functions, features, and performance required by the application.
Presented by Ron Wade, System Architect at IDT. For more information visit the PCIe clocks page.
This is the first video in our PCIe series. In this video, we define PCIe architectures, focusing on common and separate clock architectures. Watch the rest of the video series below where Ron will cover the impact of different timing architectures.
In this episode, Ron Wade from IDT (acquired by Renesas) explains PCIe common clocking and its impact on timing solutions. Learn about using a single clock source, fan-out buffers, and the considerations for spread spectrum and non-spread spectrum clocking in PCIe systems.
In this video, we explore PCIe with separate reference clocks and the effects of clock selection. Learn how separate reference clocks work and their impact on system performance and stability.
This video provides a high-level overview of Separate Reference Clock with Independent Spread (SRIS) architectures for PCI Express systems, additional performance requirements that this clocking architecture imposes on the reference clocks, and some system implications encountered trying to implement the architecture.
IDT provides a brief overview of the timing solutions optimized for various configurations using the NXP (Freescale) QorIQ / Layerscape processors.
Resources
IDT provides a brief tutorial on the timing solutions required for NXP (Freescale) QorIQ / Layerscape processor-based systems.
Presented by Ron Wade, PCI Express timing expert.
IDT (acquired by Renesas) engineer provides a brief tutorial describing the main differences between standard HCSL and low-power HCSL (LP-HCSL).
Presented by Ron Wade, PCI Express timing expert.
Related Resources
An overview of IDT's full-featured PCI Express (PCIe) clock generators addressing PCIe Gen 1, Gen 2, Gen 3, and Gen 4.
Presented by Ron Wade, System Architect at IDT.
An overview of PCI Express applications and how IDT's industry-leading portfolio of PCIe clock products addresses the requirements. The video briefly discusses PCIe riser cards, embedded SOC, and PCIe storage (NVME) examples.
Presented by Ron Wade, System Architect at IDT.
A brief overview of how data rates have changed from PCI Express (PCIe) Generation 1, Gen 2, Gen 3, Gen 4 and Gen 5.
Presented by Ron Wade, system architect at IDT. For more information about IDT's PCIe timing solutions, visit the PCI Express (PCIe) Clocks page.
A brief overview of how clock and timing specifications have changed from PCI Express (PCIe) Generation 1, Gen 2, Gen 3, Gen 4 and Gen 5.
Presented by Ron Wade, system architect at IDT (acquired by Renesas). For more information, visit Renesas's PCIe Timing Solutions page.
A brief overview of the PCI Express common clock (CC) jitter model, and the transfer functions as they relate to the timing PLLs. This model applies to PCI Express (PCIe) Gen 2, Gen 3, Gen 4 and Gen 5. The equations would be slightly different for other PCIe architectures, such as SRIS, SRnS, or data clocked.
Presented by Ron Wade, system architect at IDT (acquired by Renesas). For more information about Renesas's PCIe timing solutions, visit the PCI Express (PCIe) Clocks page.