Features
- Buck-boost NVDC charger for 1-, 2-, 3-, or 4-cell Li-ion batteries
- Input voltage range 3.2V to 23.4V (no dead zone)
- System output voltage 2.4V to 18.304V
- Autonomous charging option (automatic end of charging)
- System power monitor PSYS output, IMVP compliant
- Up to 1MHz switching frequency
- Adapter current and battery current monitor (AMON/BMON)
- PROCHOT# open-drain output, IMVP compliant
- Allows trickle charging of a depleted battery
- Ideal diode control in Turbo mode
- Reverse buck, boost, and buck-boost operation from battery
- Two-level adapter current limit available
- Battery Ship mode option
- SMBus and auto-increment I2C compatible
- 4mm x 4mm 32 Ld TQFN package
Description
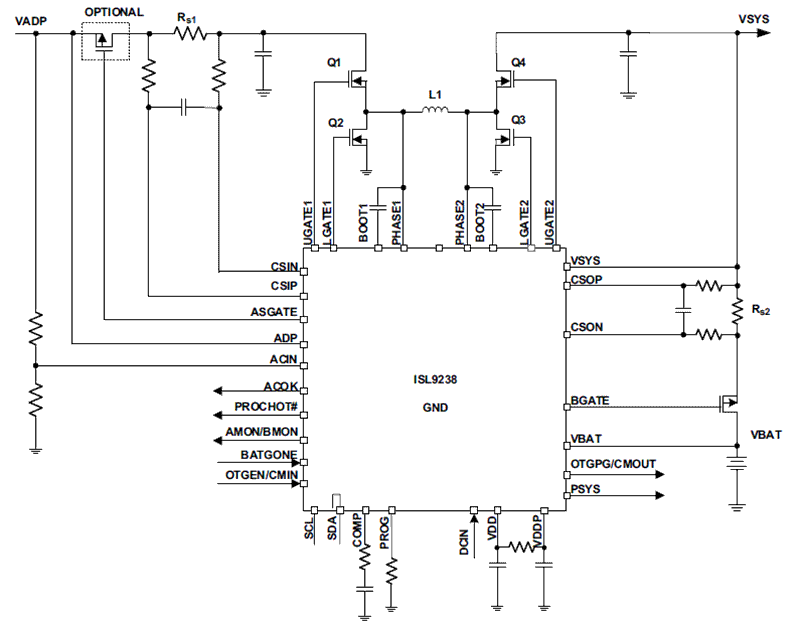
The ISL9238 is a buck-boost Narrow Output Voltage DC (NVDC) charger. The ISL9238 provides the NVDC charging, system bus regulation and protection features for tablet, Ultrabook, notebook, power bank, and any USB-C interface platform. The advanced Renesas R3™ Technology provides high light-load efficiency and fast transient response. In Charging mode, the ISL9238 takes input power from a wide range of DC power sources (such as conventional AC/DC charger adapters, USB PD ports, and travel adapters) and safely charges battery packs with up to 4-series cell Li-ion batteries. As a NVDC topology charger, it also regulates the system output to a narrow DC range for stable system bus voltage. The system power can be provided from the adapter, battery, or a combination of both. The ISL9238 can operate with only a battery, only an adapter, or both connected. For Intel IMVP8 compliant systems the ISL9238 includes System Power monitor (PSYS) functionality, which provides an analog signal representing total platform power. The PSYS output connects to a wide range of IMVP8 core regulators to provide an IMVP8 compliant power domain function. The ISL9238 supports reverse buck, boost, or buck-boost operation to input port from 2- to 4-cell batteries. The ISL9238 has serial communication using SMBus/I2C that allows programming of many critical parameters to deliver a customized solution.
Parameters
| Attributes | Value |
|---|---|
| Topology [Rail 1] | Buck-Boost |
| Input Voltage (Min) (V) | 3.2 |
| Input Voltage (Max) (V) | 23.4 |
| Input Current Limit Accuracy (% (±)) | 2 |
| Battery Charge Voltage | 2.4 to 18.304 |
| Charging Voltage Accuracy (Max) (±%) | -1.1, 0.5 |
| Battery Charge Voltage Adjustment | 8mV steps |
| Charge Current Limit Accuracy | ±2 (4A, CSOP - CSON = 60mV) |
| Trickle Charge Current Range | 64mA, 128mA, 256mA, or 512mA |
| Switching Frequency Range (Typical) (kHz) | - |
Package Options
| Pkg. Type | Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | Lead Count (#) | Pitch (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TQFN | 4.0 x 4.0 x 0.70 | 32 | 0.4 |
Applications
- 1 to 4-cell tablets
- Ultrabooks
- Notebooks
- Power banks
- Any USB-C interface portable device requiring batteries
Applied Filters:
Filters
Software & Tools
Sample Code
Simulation Models
Introducing the industry's first buck-boost battery charger supporting USB Type-C® connectors. The single-chip ISL9237 reduces BOM costs by up to 40% and extends battery life for ultrabooks, tablets, and power banks.
Transcript
The USB Type-C is a next generation industry standard that allows charging, data transfer, and video, all in one simple connector. It can deliver up to 20V or 100W over a single cable: tailored to fit mobile devices, yet robust enough for laptops and tablets. It features reversible plug orientation and cable direction, so it will no longer matter which end of the cable or which side of the connector you plug in. It is truly all-in-one connectivity standards for tablets, notebooks, or smartphones. The USB 3.1 compliant ISL9237 joins the emerging USB Type-C ecosystem as the first battery charger capable of providing buck mode, buck-boost mode, and boost mode for 1 to 3-cell lithium-ion batteries.
The single-chip ISL9237 replaces competitive buck and boost two-chip charger solutions, eliminating a charger IC and inductor, to reduce customer bill of material costs by up to 40%. It also supports USB On-The-Go (OTG) with a 5V ultra-reverse buck mode, and reduces traditional two-stage charging to a single stage buck-boost for improved efficiency. In charging mode, the ISL9237 takes input power from a wide range of DC power sources: AC/DC charger adaptors, USB power delivery ports and any travel adapter to charge battery packs with up to three series cell lithium-ion batteries.
The ISL9237 can also operate connected to only a battery, an adapter or both. The ISL9237's key features include: input voltage range of 3.2V to 23.4V, system output voltage of 2.4V to 13.1824V, up to 1MHz operation allows smaller, lower cost inductors, and reduces acoustic noise in DCM mode.
The ISL9237 battery charger is the latest member Renesas' family of mobile computing power management solutions, which include the ISL95852, Vcore PMIC, and the ISL95908 peripheral PMIC. These products power IMVP8 compliant systems using Renesas' sixth generation core processors. For more information about the ISL9237 buck-boost charger IC, please visit the ISL9237 product page.
This product training presentation of the ISL9237 and ISL9238 buck-boost battery charger solutions will give you a brief overview of the device feature set and performances. These products can operate in buck, buck-boost, and boost mode to maintain an accurate output voltage and support USB On-The-Go (OTG) with 5V reverse buck mode from the ISL9237, and full range 5V to 20V OTG from ISL9238.
Transcript
ISL9237 USB-CTM Buck-Boost Battery Charger
Welcome to the product training presentation of the ISL9237 buck-boost battery charger. This presentation will give you a brief overview of the device feature set and performances.
Emerging USB-C Replaces Existing USB Technology
The year 2015 opened up a new era of power management as high-profile devices began to adopt USB-C ports. A true all-in-one port, it is capable of delivering bidirectional data and power at the same time. USB-C charging requires a fundamental change to the existing power delivery architecture and presents a new challenge to system designers. With a default 5V voltage, the USB-C port is capable of negotiating with the plugged-in device to raise the port voltage to 12V, 20V, or another mutually agreed on voltage, at a mutually agreed current level. The maximum power a USB-C port can deliver is 20V at 5A current, which is 100W of power.
Introducing the ISL9237 USB-C Buck-Boost Battery Charger
The ISL9237 is the industry’s first USB-C buck-boost charger. It provides two-way power delivery while using a single-chip technology that reduces BOM costs and improves efficiency. It can operate in buck, buck-boost, and boost mode to maintain an accurate output voltage and supports USB On-The-Go (OTG) with a 5V reverse buck mode.
Furthermore, it achieves acoustic noise-free operation, superior light load efficiency and fast dynamic response thanks to Intersil’s patented R3 modulation.
ISL9237 USB-C Buck-Boost Battery Charger Typical Application
The ISL9237 has an input voltage range of 3.2V to 23.4V with an output of 2.4V to 13.824V for 1 to 3-cell batteries. Automatic sensing allows the device to enter trickle charging mode when the battery is depleted, and battery learn mode calibrates the battery fuel gauge. Programmable features using the SMBus or I2C interface provide the user with flexibility in their design.
Buck-Boost Charger Solutions
Traditional non-inverting buck-boost circuits use two controllers to achieve a wide output voltage. The converters may be in series or in parallel with a switch to select the active controller. These solutions require two controllers and inductors, cannot operate in the reverse direction, and in the case of the series configuration, are less efficient. Intersil’s latest single chip solution for USB-C addresses all the power requirements while using a single inductor and controller, while also providing additional features.
ISL9237 Buck-Boost Charger with USB On-The-Go (OTG) Function
The ISL9237 consists of four switching FETs and an inductor, as well as a battery connecting FET (BFET). The four switching FETs are grouped into a forward-buck leg and a forward-boost leg. By operating either leg, this topology can operate in forward buck mode or forward boost mode for charging the battery. It can also operate in reverse buck mode to deliver power out of the USB port for charging an external electronic device.
Autonomous Operational Mode Decisions
The device monitors the input and output voltage to determine the correct mode of operation, and switches between each mode to maintain a stable output voltage.
Intersil Solution Eliminates Acoustic Noise
Thanks to the R3 modulator, the ISL9237 delivers the smallest energy transfer per cycle, resulting in no acoustic noise. Competitor parts use larger bursts to transfer energy, resulting in an audible hum.
Inrush Current Control
Another feature of the device is an optional ability to control inrush current. The ASGATE pin of the ISL9237 will drive a FET to control the current for a minimal startup current.
2-Level Adapter Current Limit
The ISL9237 also provides a two-level adapter current limit with fully programmable magnitudes and durations to take advantage of the adapter’s surge current capability.
EVB Efficiency, L = 2.2µH, Fs = 1MHz
Taking a look at the efficiency, the ISL9237 impresses with up to 97% peak efficiency and over 90% efficiency in the majority of cases.
ISL9237 Applications
One of the leading applications for the ISL9237 is the power bank. These devices are a newly emerging product with a two-cell battery that are charged with USB-C and can then be used as a battery pack for other devices either through USB-C or traditional USB-A/B.
There are numerous additional applications for the ISL9237 as more and more products embrace USB-C ports. The ISL9237 is already in many reference designs and used by many customers in production.
Supporting Material
Supporting material for the ISL9237 includes a datasheet, the ISL9237EVAL2Z evaluation board and user’s guide, a white paper, and video. The datasheet includes all relevant information to use the device.
Summary
In summary, the ISL9237 is the industry’s first USB-C buck-boost battery charger, capable of delivering buck, buck-boost, and boost for 1 to 3-cell batteries as well as 5V reverse buck-mode for USB On-The-Go. It also provides numerous hardware and programmable features, all at very high efficiencies.
Learn how to set up the ISL9237 evaluation board and connect the EVB to the GUI interface. Add an electrical load and measure output voltage and phase voltages without the need for a Li-Ion battery or emulator.
Transcript
ISL9237 Evaluation Board and GUI Demonstration
Hi, I'm Phil Brinkley, Central Applications Engineer with Intersil. Today I'd like to talk to you about the ISL9237 Eval Kit. When your order the kit, you'll receive a box like this one. In the box, it contains the board itself, USB stick with the necessary software, and some documentation on the user's manual for the board itself. You'll want to load the software, but for now I'm going to begin by demonstrating without the need of the software.
So what you need for the first part to check out and make sure your board is actually working is the board, you need a power supply, and some cabling, and oscilloscope nice to have but not necessary, and you need a multimeter.
Measure Output Voltage
So what we first want to do is connect the power supply to the board. Do that by connecting the ground to J2. And the positive to J1.
I'm going to turn my power supply on, and connect it to 5V.
As soon as you have it up and running, and the output is set to 5V. I'm going to measure the output voltage across VSYS, that is the upper right hand output connectors on the right. J3 and J4, and it should measure 8.39V or 8.38V somewhere in that neighborhood, if so, the board is working properly.
The second thing you can do without having to load any of the software is to add an oscilloscope in, and measure the phase voltages. So I'm measuring phase one, and phase two on the ISL9237 itself. So what I'm going to do now is increment my voltage output from 5V in, all the way up to about 15V, and then back down. As I do, you'll see the phase voltages change, and that will indicate the difference between boost mode, because right now we have 5V coming in, and 8V coming out, or more than 8V coming out.
We're on boost mode, and then it's going to move into buck-boost mode, and eventually move into buck mode.
And so you want to see that if you have an oscilloscope, you can just slowly ramp the voltage up.
When I get to about 7V or 8V, it begins to move into buck-boost mode. I started off in the boost mode, and when I get above 11V or so. It'll move into pure buck mode. So you can see the phases change.
So those two things are easy to do right out of the box, and you can make sure your board is working.
Using ISL9237EVAL2Z GUI Software
Next thing you can do is add the software piece in. You'll find that under start button, all programs, Intersil, and then the program name itself is called ISL9237 SMBus tool C3.
If you have any issues installing the software, go to the ISL9237 product page, click under the resources tab, we have some FAQs, they help walk you through, maybe issues that you might run into a driver or such.
We need a mini USB cable. Plug the cable in to the board. Once you have that connected, you want to make sure that your computer is talking over USB to the ISL9237.
So you want to confirm on the upper right hand corner of the software that you have a green check mark. Right now, I have a red X box, so it means it's not connected. So I'm going to click on reset USB. And in my case everything is connected right, and the green check mark is now on.
To verify that your software is connected actually to your board, go to manufacturer ID, click read, and you should see 0049 for manufacturer ID. That's identified in the datasheet.
Last thing you might want to try is to add a load to the output. Now loads can be a lot of different things, if you have a battery emulator that would be probably one of the best things you could use. You might actually power a rechargeable lithium ion battery. In my case, I'm just going to use a 1Ω power resistor. It's a cheap and dirty way to make sure that the device is doing what you think it's doing.
So I'm going to connect that to the VBAT, which is the bottom right hand output connector. It's J5 and J6.
In the software, choose one cell under battery cell configuration. I'm going to hit right all and then I'm going to measure the voltage across the battery which is the power resistor.
Right now, I'm reading 0V, that's to be expected because the default in the software is 0A on the charge current limit. If I change the charge current limit to say something like 1A, and click write all, the output voltage jumps to 1V, makes sense. I've got a 1Ω resistor, and I'm feeding 1A through it. I have 1V across.
So that demonstrates getting started quickly with the ISL9237 Eval Kit. There's a lot of different things you can do in the software, and with the kit. Go to our website and refer to the user's manual for further demos that can be done with this. Thanks for watching.