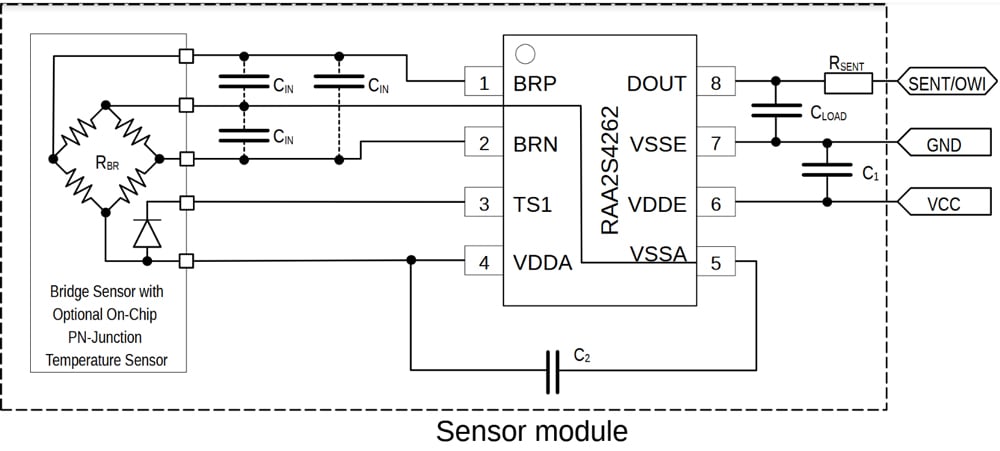
Features
- Differential bridge sensor input with selectable on-chip or external temperature sensor – PTC, NTC, PN-junction, and sensor bridge resistance
- 1mV/V to 800mV/V sensor span with 12 to 18-bit resolution
- Compensation for offset, gain, and higher order nonlinearity and temperature coefficients of measured bridge sensor input signal
- Accuracy:
- 0.5%FS at -40 °C to +125 °C
- 1%FS at -40 °C to +155 °C
- Internal output update rate up to 200µs in the fastest mode
- Compliant with SENT standard SAE J2716 Rev. 4 (APR2016), tick time extended to 1µs resulting in a SENT output time of 282µs (two fast channels)
- Third order digital LPF with a cut-off frequency of 10Hz to 1000Hz
- Fast in calibration: one-pass, end-of-line calibration algorithm minimizes production costs
- Minimum number of external components enables the design of sensor modules with best-in-class form factor
- Qualified according to AEC-Q100 Grade 0
- Operating temperature range of -40 °C to +155 °C with up to 100hrs extension up to +165 °C
Description
The RAA2S4266 is a top-tier automotive sensor signal conditioner (SSC) with SENT, designed for precise amplification and correction of differential bridge sensor signals. It offers exceptional precision and reliability with outstanding analog pre-amplification and sensor offset correction, making it adaptable to nearly all resistive bridges. The advanced signal processing utilizes a 16-bit RISC microcontroller for accurate conditioning calculations, and data stored in nonvolatile memory. Reliable data transmission is ensured through a digital SENT interface, providing dependable transmission via a single output pin. Built for tough environments, the product features robust protection circuitry, excellent electromagnetic compatibility, and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. Additionally, the RAA2S4266 supports end-of-line calibration and offers an OWI interface for straightforward configuration and calibration.
Parameters
| Attributes | Value |
|---|---|
| Function | Resistive SSC |
| Automotive Qual. | Yes |
| Supply Voltage (V) | 4.5 - 5.5 |
| Input Type | Single-bridge |
| Interface | SENT |
| Adj. Analog Gain | 1 - 912 |
| Resolution (bits) | 18 |
| Sample Rate Max (KHz) | 5 |
| Temp. Range (°C) | -40 to +165°C |
Package Options
| Pkg. Type | Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | Lead Count (#) | Pitch (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOIC | 4.9 x 3.9 x 1.5 | 8 | 1.27 |
Product Comparison
| RAA2S4266 | ZSSC4161 | ZSSC4162 | ZSSC4165 | ZSSC4169 | |
| Function | Resistive SSC | Resistive SSC | Resistive SSC | Resistive SSC | Resistive SSC |
| Automotive Qual. | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Supply Voltage | 4.5 - 5.5 | 4.5 - 5.5, 4.75 - 5.25 | 4.5 - 5.5 | 4.5 - 5.5, 4.75 - 5.25 | 4.5 - 5.5, 4.75 - 5.25 |
| Input Type | Single-bridge | PTC, Single-Bridge, Single-bridge, Temperature Diode | NTC, PTC, Single-Bridge, Temperature Diode | Dual-Bridge, Dual-bridge, NTC, PTC, Temperature Diode | Single-Bridge, Single-bridge, Temperature Diode |
| Interface | SENT | I2C, SENT | I2C, SENT | I2C, SENT, ZACwire™ | I2C, SENT |
| Adj. Analog Gain | 1 - 912 | 1 - 200, 2.1 - 200 | 1 - 200 | 1 - 200, 2.1 - 200 | 2.1 - 200 |
| Resolution (bits) | 18 | 14-18, 18 | 14-18 | 14-18, 18 | 14 |
| Sample Rate Max (KHz) | 5 | 1.33, 1.48 | 1.45 | 0.9, 1.16 | 0.66, 1.3 |
| Temp. Range (°C) | -40 to +165°C | -40 to +150°C | -40 to +150°C | -40 to +150°C, 0 to +70°C | -40 to +150°C, -40 to 150°C |
Applications
- Pressure sensing in engine control systems
- Hydraulic and pneumatic system monitoring
- HVAC pressure measurement
- Automotive sensor signal conditioning
- Industrial automation and control systems
Applied Filters:
Filters
Software & Tools
Sample Code
Simulation Models
The RAA2S426x are top-tier automotive sensor signal conditioners (SSCs) with SENT or I²C output, designed for precise amplification and correction of differential bridge sensor signals. The devices offer exceptional precision and reliability with outstanding analog pre-amplification and sensor offset correction, making them adaptable to nearly all resistive bridges.
News & Blog Posts
Blog Post
May 1, 2025
|