Features
- 8 - 0.7 V current-mode differential output pairs
- Supports zero delay buffer mode and fanout mode
- Bandwidth programming available
- Spread spectrum modulation tolerant, 0 to -0.5% down spread and +/- 0.25% center spread.
- Supports undriven differential outputs in PD# and SRC_STOP# modes for power management.
- Supports polarity inversion to the output enables, SRC_STOP and PD.
- Outputs cycle-cycle jitter < 50 ps
- Outputs skew: 50 ps
- 50 - 200 MHz operation
- Extended frequency range in bypass mode to 400 MHz
- PCI Express® Gen I compliant
- Real time PLL lock detect output pin
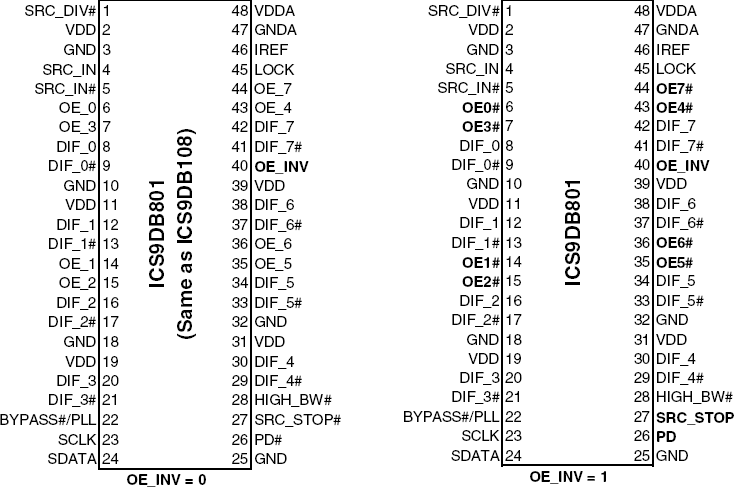
- 48-pin SSOP/TSSOP package
- Available in RoHS compliant packaging
Description
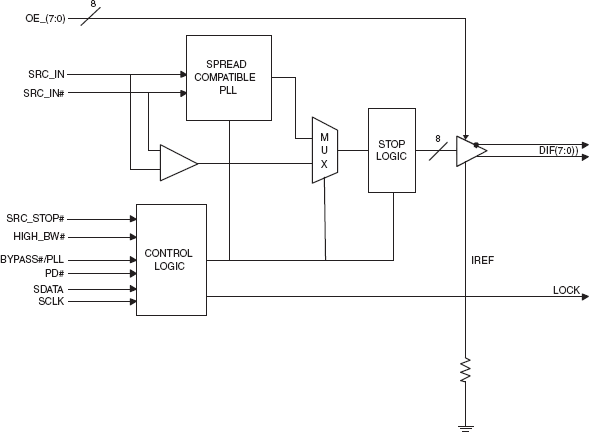
The 9DB801C is a DB800 Version 2.0 Yellow Cover part with PCI Express® support. It can be used in PC or embedded systems to provide outputs that have low cycle-to-cycle jitter (50 ps), low output-to-output skew (100 ps), and are PCI Express® gen 1 compliant. The 9DB801C supports a 1 to 8 output configuration, taking a spread or non spread differential HCSL input from a CK410(B) main clock such as 954101 and 932S401, or any other differential HCSL pair. 9DB801C can generate HCSL or LVDS outputs from 50 to 200 MHz in PLL mode or 0 to 400 MHz in bypass mode. There are two de-jittering modes available selectable through the HIGH_BW# input pin, high bandwidth mode provides de-jittering for spread inputs and low bandwidth mode provides extra de-jittering for non-spread inputs. The SRC_STOP#, PD#, and individual OE# real-time input pins provide completely programmable power management control.
Applied Filters:
Filters
Software & Tools
Sample Code
Simulation Models
This is the first video in our PCIe series. In this video, we define PCIe architectures, focusing on common and separate clock architectures. Watch the rest of the video series below where Ron will cover the impact of different timing architectures.
In this episode, Ron Wade from IDT (acquired by Renesas) explains PCIe common clocking and its impact on timing solutions. Learn about using a single clock source, fan-out buffers, and the considerations for spread spectrum and non-spread spectrum clocking in PCIe systems.
In this video, we explore PCIe with separate reference clocks and the effects of clock selection. Learn how separate reference clocks work and their impact on system performance and stability.
This video provides a high-level overview of Separate Reference Clock with Independent Spread (SRIS) architectures for PCI Express systems, additional performance requirements that this clocking architecture imposes on the reference clocks, and some system implications encountered trying to implement the architecture.