Features
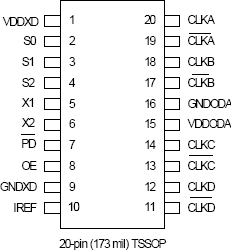
- Packaged in 20-pin TSSOP
- RoHS 5 (green) or RoHS 6 (green and lead free) complaint package
- Supports PCI-Express applications
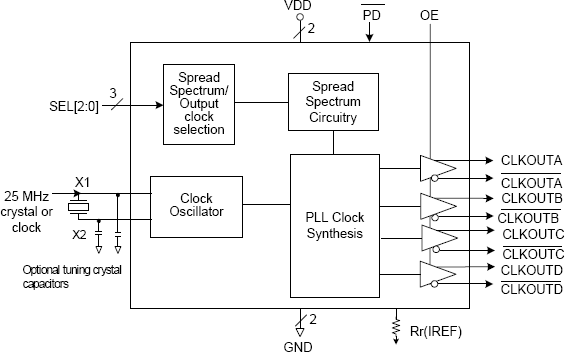
- Four differential spread spectrum clock outputs
- Spread spectrum for EMI reduction
- Uses external 25 MHz clock or crystal input
- Power down pin turns off chip
- OE control tri-states outputs
- Spread and frequency selection via external pins
- Spread Bypass option available
- Industrial temperature range available
- For PCIe Gen2 applications, see the 5V41066
- For PCIe Gen3 applications, see the 5V41236
Description
The 557-05A is a spread-spectrum clock generator that supports PCI-Express requirements. It is used in PC or embedded systems to substantially reduce electro-magnetic interference (EMI). The device provides four differential HCSL or LVDS high-frequency outputs with spread spectrum capability. The output frequency and spread type are selectable using external pins.
Parameters
| Attributes | Value |
|---|---|
| Temp. Range (°C) | -40 to 85°C, 0 to 70°C |
Package Options
| Pkg. Type | Pkg. Dimensions (mm) | Lead Count (#) | Pitch (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TSSOP | 6.5 x 4.4 x 1.0 | 20 | 0.65 |
Applied Filters:
Filters
Software & Tools
Sample Code
Simulation Models
This is the first video in our PCIe series. In this video, we define PCIe architectures, focusing on common and separate clock architectures. Watch the rest of the video series below where Ron will cover the impact of different timing architectures.
In this episode, Ron Wade from IDT (acquired by Renesas) explains PCIe common clocking and its impact on timing solutions. Learn about using a single clock source, fan-out buffers, and the considerations for spread spectrum and non-spread spectrum clocking in PCIe systems.
In this video, we explore PCIe with separate reference clocks and the effects of clock selection. Learn how separate reference clocks work and their impact on system performance and stability.
This video provides a high-level overview of Separate Reference Clock with Independent Spread (SRIS) architectures for PCI Express systems, additional performance requirements that this clocking architecture imposes on the reference clocks, and some system implications encountered trying to implement the architecture.