GreenPAK family devices that include the Asynchronous State Machine (ASM) macrocell allow the user to develop their own custom state machine designs. The user has the option to set the definition of the states, the definition of allowed state transitions, and the definition of the signals that will trigger each state transition. This macrocell can also be flexibly connected to I/O pins and other GreenPAK resources for state transition inputs, and outputs from the macrocell can be routed to other resources or I/O pins. Two important performance parameters for this macrocell are transition times of less than 1µS from state to state, and a standby current of less than 1µA when not in active state transition.
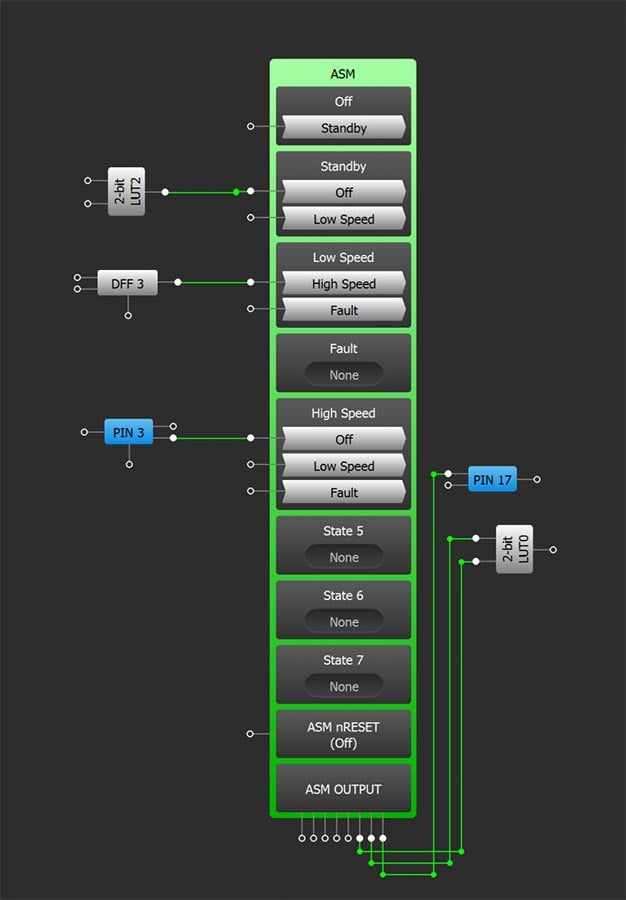
This ASM macrocell is supported in an ASM Editor window in the GreenPAK Designer software. Shown here is the view inside the ASM Editor. This editor supports the flexibility to:
- Checkboxes to select states in the project, up to the allowable maximum number of states based on silicon architecture
- Edit state names to match the application
- Easy “point and click” actions to add state transitions
- Arrange the state diagram for best comprehension
- Set the value of output signals in the Output RAM Array
Inside the main GreenPAK Designer GUI, the ASM macrocell shows up with inputs that drive state transitions, and outputs that can be routed to other internal resources or out to pins. Inside each state, the allowed “next states” show up here, with an input that, when asserted, will cause that state transition to happen. The connection between resources used to make state transitions and the state transition links is also shown back in the original ASM Editor window, with labels on each of the state transition signals showing the source of the signal.
As this macrocell does not require a clock input, it will consume less than 1µA when not in active state transition. This gives the designer tremendous flexibility to create low power designs in minutes. This is especially valuable when designing event-driven systems that are waiting long periods of time with little activity, as the ASM macrocell can remain in a low power state waiting for input, and react in less than a µS to change state.