The Internet of Things (IoT) has the capability of amassing large amounts of data which it does with the help of dispersed intelligent sensors. The organization and distribution of this enormous amount of data is posing to be a challenge. While conventional methods of data analysis have facilitated the operations in IoT, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has proven that it can do it with greater precision and that too in a lesser timeframe.
The role that AI plays in structuring data is phenomenal. AI is capable of spotting patterns and inconsistencies in real-time. AI algorithms can save significant time by accumulating unstructured data from various sources and processing it in a way so it can be represented in a consistent manner. This makes the process of structuring the data less arduous, thereby offering greater benefit to the stakeholders.
Machine Learning and AI are vital tools that provide secure and predictive analytics in the data center and beyond. As a result of these predictions, AI will be capable of preventing issues even before they arise, restructuring operations, and reducing unforeseen interruptions in the network. Artificial Intelligence when combined with data science can assist in structuring a data set, enhance the operations of IoT devices and ultimately reach conclusions in real-time.
AI Coupled with Real-time Analytics
In broad terms, real-time analytics refers to the process of preparing, analyzing and assessing data as soon as it is available. AI coupled with real-time analytics has provided businesses with exceptional insight into the consumer experience. The support personnel and IT workers are now prone to act rather than react, resolving issues before end users even know there is an issue to report. Hence the combination of the two has completely transformed the support experience.
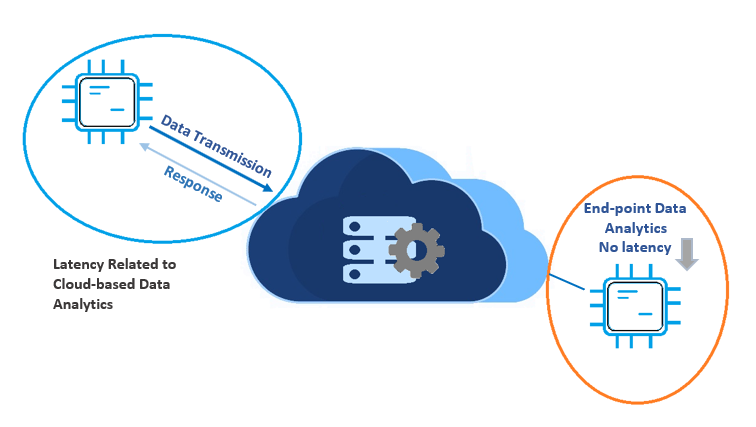
According to IDC, an analytics firm, 45% of IoT-created data needs to be analyzed closer to the end devices, rather than transmitted to be examined on the cloud. There are several reasons for the shift from the cloud. Transferring data to the cloud has proven to be costly as it requires bandwidth and power to support an interminable data transmission. There is also a potential for latency as a lot of time is expended during transmission and the necessity for a high server capacity that can handle the data that is coming. There are also instances where the endpoints lack a stable internet connection, and the decision must be made on the endpoint. That is why there is a need for solutions that can support using the analytics at the endpoint. These concerns are of great significance in IoT applications as there is a high dependency on data analytics and real-time decision making and these applications cannot afford to be dormant.
Endpoint AoT
‘Analytics of Things’ (AoT) is a term that is used to describe the analysis of data that is generated by the Internet of Things devices. The IoT Analytics of Things makes it possible to operate business intelligence within an application rather than a data warehouse. AoT assists in understanding patterns and analysis for variations, detects anomalies, predicts problems, sets maintenance intervals, and optimizes processes.
Over the years, organizations have been relying on data analytics based on centralized architecture for their data-driven planning and future vision. The data is increasing every second and there is a requirement for a revolutionary approach to overcome data transfer latency, improve privacy, and meet customer expectations. The real-time response has especially become important after the convergence of AI, 5G and IoT. All that drives us to develop intelligence at the endpoint.
Distributing intelligence across the most end of the network provides an opportunity for more efficient data analytics and make decisions in real time, with almost no latency, on the end devices. The solution that can do this with the low processing capabilities, direct on the end devices, is referred to as “Endpoint Data Analytics”.
What is “Data Analytics”?
“Data Analytics” is the science of scrutinizing raw or unprocessed data to derive meaning from it so it can be applied to decision making. Data analytics employs several modern techniques and tools that assist it in structuring and comprehending the data.
There are several steps that need to be applied in the process before the actual data analytics can take place:
- The data needs to be interpreted correctly so it may be grouped accordingly.
- Data needs to be collected from various sources
- Data needs to be scrutinized to get rid of any replication or errors.
- Data organization may be done by using tables, spreadsheets and numerous statistical methods.
According to Gartner, Data analytics can be categorized into four main types.
Descriptive Analytics
This describes what has happened over a period. It focuses on summarizing past data to make
inferences.
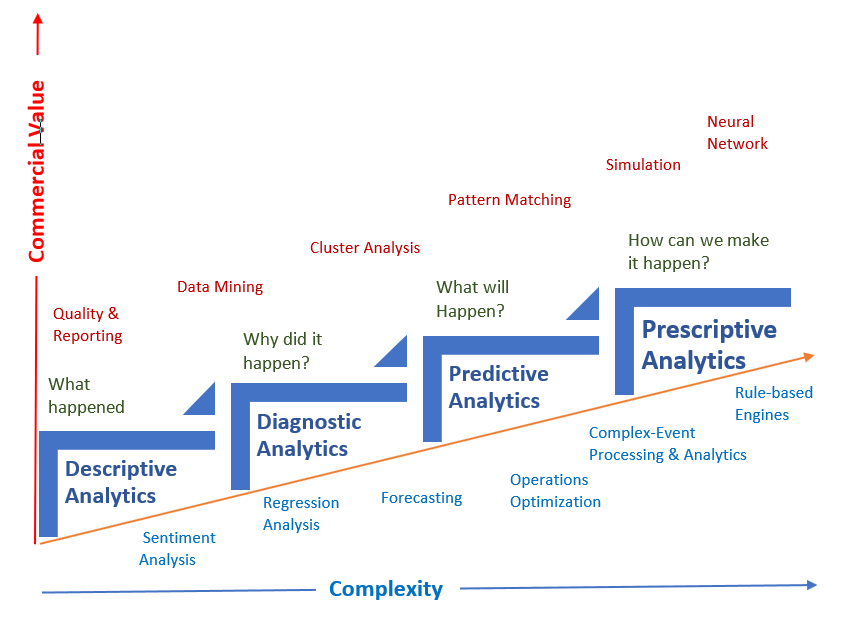
Diagnostic Analytics
It focuses on understanding and providing answers to why something occurred.
Predictive Analytics
It identifies future trends based on given data.
Prescriptive Analytics
It allows you to make recommendations of what action should be taken.
Support System of Data Analytics
Various technologies and sensors facilitate the process of data analytics at the endpoint. Sensors are required to gather and accumulate data to assist in understanding the environment. Examples of sensors include GPS for detecting locations, cameras, lasers and radars, to name a few. Communication technologies assist in transmitting and obtaining the data. The data fuels Data science algorithms which then play a vital part in comprehending the situation. The results from the algorithm processing support the decision-making process. The outcomes of the analytic data can be set as choices on the devices. For instance, the autonomous vehicle has the option of several decisions such as following a planned route, responding to other vehicles on the road, reacting to weather and road conditions and even taking an indirect command if a sudden stop can’t be done safely.
To improve the decision-making process, Data analytics will classify the decisions and actions into specific classes. For example, in the case of the autonomous vehicle, it can be defined as an operational or tactical class, or strategic in the case of the data lake.
Makeover of the Business Model
The developments in Data Analytics and AI have transformed the business face completely. Real-time analytics responds to the data collected immediately, thereby retrieving a much higher value from it. Data analytics transforms big enterprise data into a treasure trove of unlimited value. This has strengthened business value and may enable enterprises to secure a high position in the marketplace. Businesses in all sectors are relying on machine learning models to make more precise predictions and effective decisions. This has improved production efficiency and assisted in overcoming security issues in device communications as well. Endpoint AI has enhanced the entire process at many levels by speeding up the work, providing better results, automations, and improved business decision-making. Artificial Intelligence, Data Analytics and IoT all individually contribute to enhance the business model and when integrated, they are proving to be an asset to the companies.
Find information on products and technologies to help you implement AI solutions at renesas.com/AI.
