Package Information
| CAD Model: | View CAD Model |
| Pkg. Type: | SOIC-8 |
| Pkg. Code: | |
| Lead Count (#): | 8 |
| Pkg. Dimensions (mm): | |
| Pitch (mm): |
Environmental & Export Classifications
| Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) | 1 |
| Pb (Lead) Free | |
| ECCN (US) | |
| HTS (US) |
Product Attributes
| Lead Count (#) | 8 |
| Moisture Sensitivity Level (MSL) | 1 |
| Temp. Range (°C) | -40 to +125°C |
| Advanced Features | EZ-EMI, Fast DLR, PrimAccurate |
| Application | Adapters, Chargers, Home Appliances, Networking |
| Control Mode | Primary-Side Regulation Peak Current Mode DCM |
| Controller / Integrated | Controller |
| FET Driver Output Current (Max) (A) | 0.75 |
| No Load Power (mW) | 20 |
| Output Power (Min) (W) | 5 |
| Output Power Max (W) | 25 |
| PWMs (#) | 1 |
| Parametric Category | Flyback & Forward Controllers |
| Pass Device | FET |
| Pkg. Type | SOIC-8 |
| Protection Features | OVP/OTP (w/o Latch), OVP, IUVP, PCL/OCP, SRSC |
| Qualification Level | Standard |
| Switching Frequency (KHz) | 79 - 79 |
| Topology Characteristic | Flyback |
| UVLO Falling (V) | 6.5 |
| UVLO Rising (V) | 12 |
| VBIAS (Max) (V) | 16 |
Resources for iW1762
Description
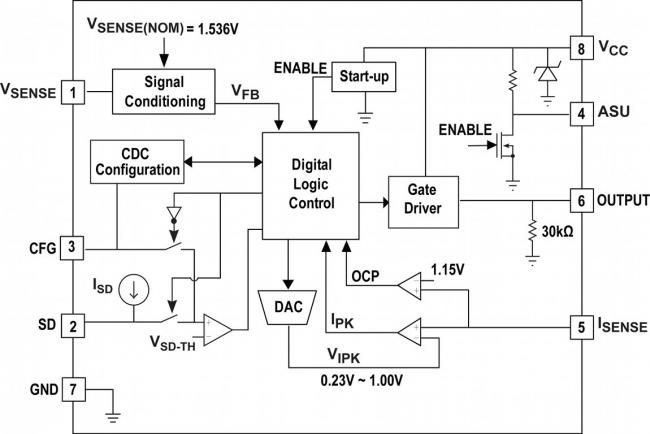
The iW1762 is a high-performance AC/DC controller designed to drive an external power N-channel MOSFET for peak current mode PWM flyback power supplies. Optimized for power supplies with output power between 15W to 24W, the iW1762 is ideal for power adapters in networking equipment and monitors.
The iW1762 easily meets the US DoE’s external power supply standard and the EU’s Code of Conduct, Version 5, Tier 2 standard, with no-load power consumption less than 20mW while complying with active mode efficiency requirements. As a PrimAccurate™ controller, the iW1762 does not need any direct secondary-side feedback components, eliminating the need for optocouplers, and reducing component count and solution cost. Additional features include Renesas' proprietary EZ-EMI™ technology, adaptive multi-mode PWM/PFM control for optimal efficiency across all loads, five selectable cable and connector voltage drop compensation voltages, and robust operation with full protection from overvoltage and overtemperature.